复杂链表的复制
题目:
请实现函数 ComplexListNode clone(ComplexListNode pHead),复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 sibling 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。节点的定义如下:
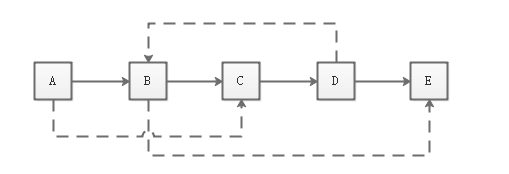
public class ComplexListNode { public int value; public ComplexListNode next; public ComplexListNode sibling; }下图是一个含有5个节点的复杂链表。图中的实线箭头表示 next 指针,虚线箭头表示 sibling 指针。为简单起见,指向 null 的指针没有画出。
分析:
第一反应是先复制原链表的每个节点,使用 next 将它们连接起来;然后找到每个节点的 sibling 对应的节点,再用 sibling 连接。对于一个含有 n 个节点的链表,由于定位每个节点的 sibling 都需要从链表的头节点开始经过 O(n) 步才能找到,因此这种方法时间复杂度是 O(n^2)
第二种办法是,遍历链表的时候把每个节点对应的 sibling 保存起来,比如哈希表,这样就可以通过 O(1) 的时间复杂度找到每个节点的 sibling。对于一个含有 n 个节点的链表,需要一个 O(n) 大小的哈希表,时间复杂度变为 O(n),相当于空间换时间。
有没有一种办法,在不需要额外空间的情况下实现 O(n) 的时间复杂度?
这个方法总共分三步:
第一步把原始链表中每个节点 N 创建对应的 N',然后连接在 N 的后面。这一步完成之后如下图所示:

第二步设置复制出来节点的 sibling。假设原链表上 N 的 sibling 指向节点 S,那么其对应复制出来的 N' 是 N 的next 指向的节点,则 S' 也是 S 的 next 指向的节点。设置 sibling 后如下图所示:

第三步把这个长链表拆分成两个链表。把奇数位置的节点用 next 连接起来就是原始链表,把偶数节点用 next 连接起来就是复制出来的链表。拆分后链表如下图所示

代码:
public class CloneComplexLinkedList {
public static ComplexListNode clone(ComplexListNode pHead) {
cloneNodes(pHead);
connectSiblingNodes(pHead);
return reconnectNodes(pHead);
}
/**
* 复制链表的节点
*
* @param pHead 链表头节点
*/
public static void cloneNodes(ComplexListNode pHead) {
// 1->2
// 1->1'->2
ComplexListNode pNode = pHead;
while (pNode != null) {
ComplexListNode pClone = new ComplexListNode();
pClone.value = pNode.value;
pClone.next = pNode.next;
pClone.sibling = null;
pNode.next = pClone;
pNode = pClone.next;
}
}
/**
* 连接链表的 sibling 指针
*
* @param pHead 链表头节点
*/
public static void connectSiblingNodes(ComplexListNode pHead) {
ComplexListNode pNode = pHead;
while (pNode != null) {
ComplexListNode pClone = pNode.next;
if (pNode.sibling != null) {
pClone.sibling = pNode.sibling.next;
}
pNode = pClone.next;
}
}
/**
* 把长链表分成两个短链表
*
* @param pHead 链表头节点
* @return 复制的链表
*/
public static ComplexListNode reconnectNodes(ComplexListNode pHead) {
ComplexListNode pNode = pHead;
ComplexListNode cloneHead = null;
ComplexListNode cloneNode = null;
if (pNode != null) {
cloneHead = cloneNode = pNode.next;
pNode.next = cloneNode.next;
pNode = pNode.next;
}
while (pNode != null) {
cloneNode.next = pNode.next;
cloneNode = cloneNode.next;
pNode.next = cloneNode.next;
pNode = pNode.next;
}
return cloneHead;
}
}
测试:
public class TestCloneComplexLinkedList {
ComplexListNode head = new ComplexListNode(1);
@Before
public void before() {
ComplexListNode node2 = new ComplexListNode(2);
ComplexListNode node3 = new ComplexListNode(3);
ComplexListNode node4 = new ComplexListNode(4);
ComplexListNode node5 = new ComplexListNode(5);
ComplexListNode node6 = new ComplexListNode(6);
ComplexListNode node7 = new ComplexListNode(7);
head.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
node5.next = node6;
node6.next = node7;
head.sibling = node4;
node2.sibling = node6;
node5.sibling = node3;
node7.sibling = node4;
}
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(head));
ComplexListNode cloneHead = CloneComplexLinkedList.clone(head);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(cloneHead));
}
}