sentinel分布式限流及熔断
Sentinel整合Dubbo限流实战
Sentinel-provider 生产者
添加jar依赖
<dependency>
<artifactId>sentinel-api</artifactId>
<groupId>com.gupaoedu.sentinel</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>2.7.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
SentinelService
public interface SentinelService {
String sayHello(String name);
}
SentinelServiceImpl
@Service
public class SentinelServiceImpl implements SentinelService{
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("begin execute sayHello:"+name);
return "Hello World:"+name+"->timer:"+LocalDateTime.now();
}
}
DubboConfig
@Configuration
@DubboComponentScan("com.gupao.sentinel")
public class DubboConfig {
@Bean
public ApplicationConfig applicationConfig() {
ApplicationConfig applicationConfig = new ApplicationConfig();
applicationConfig.setName("sentinel-dubbo");
applicationConfig.setOwner("zhangsan");
return applicationConfig;
}
@Bean
public RegistryConfig registryConfig() {
RegistryConfig registryConfig = new RegistryConfig();
registryConfig.setAddress("zookeeper://172.16.11.128:2181");
return registryConfig;
}
@Bean
public ProtocolConfig protocolConfig() {
ProtocolConfig protocolConfig = new ProtocolConfig();
protocolConfig.setName("dubbo");
protocolConfig.setPort(20880);
return protocolConfig;
}
}
容器启动方式
Bootstrap
public class Bootstrap{
public static void main( String[] args ) throws IOException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext=
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DubboConfig.class);
((AnnotationConfigApplicationContext) applicationContext).start();
System.in.read();
}
}
Sentinel-web 消费者
添加jar依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.7.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>2.7.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<artifactId>sentinel-api</artifactId>
<groupId>com.gupaoedu.sentinel</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
SentinelController
@RestController
public class SentinelController {
@Reference
private SentinelService sentinelService;
@GetMapping("/sayHello")
public String sayHello() {
return sentinelService.sayHello("zhangsan");
}
}
application.properties
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://172.16.11.128:2181
dubbo.scan.base-packages=com.gupao.sentinel.sentinelweb
dubbo.application.name=sentinel-web
添加sentinel限流支持
添加jar包依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-dubbo-adapter</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
设置限流的基准
Service Provider 用于向外界提供服务,处理各个消费者的调用请求。为了保护 Provider 不被激增的流量拖垮影响稳定性,可以给 Provider 配置 QPS 模式的限流,这样当每秒的请求量超过设定的阈值时会自动拒绝多的请求。限流粒度可以是服务接口和服务方法两种粒度。若希望整个服务接口的 QPS 不超过一定数值,则可以为对应服务接口资源(resourceName 为接口全限定名)配置 QPS 阈值;若希望服务的某个方法的 QPS 不超过一定数值,则可以为对应服务方法资源(resourceName 为接口全限定名:方法签名)配置 QPS 阈值
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
initFlowRule();
SpringApplication.run(SentinelProviderApplication.class, args);
System.in.read();
}
private static void initFlowRule(){
FlowRule flowRule=new FlowRule();
//针对具体的方法限流
flowRule.setResource(
"com.gupao.sentinel.dubbo.api.SentinelService:sayHello(java.lang.String)");
flowRule.setCount(10);//限流阈值 qps=10
flowRule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);//限流阈值类型(QPS 或并发线程数)
flowRule.setLimitApp("default");//流控针对的调用来源,若为 default 则不区分调用来源
//流量控制手段(直接拒绝、Warm Up、匀速排队)
flowRule.setControlBehavior(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(Collections.singletonList(flowRule));
}
启动时加入 JVM 参数 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8080 指定控制台地址和端口
使用jmeter进行压测
配置50个线程同时请求 /sayHello
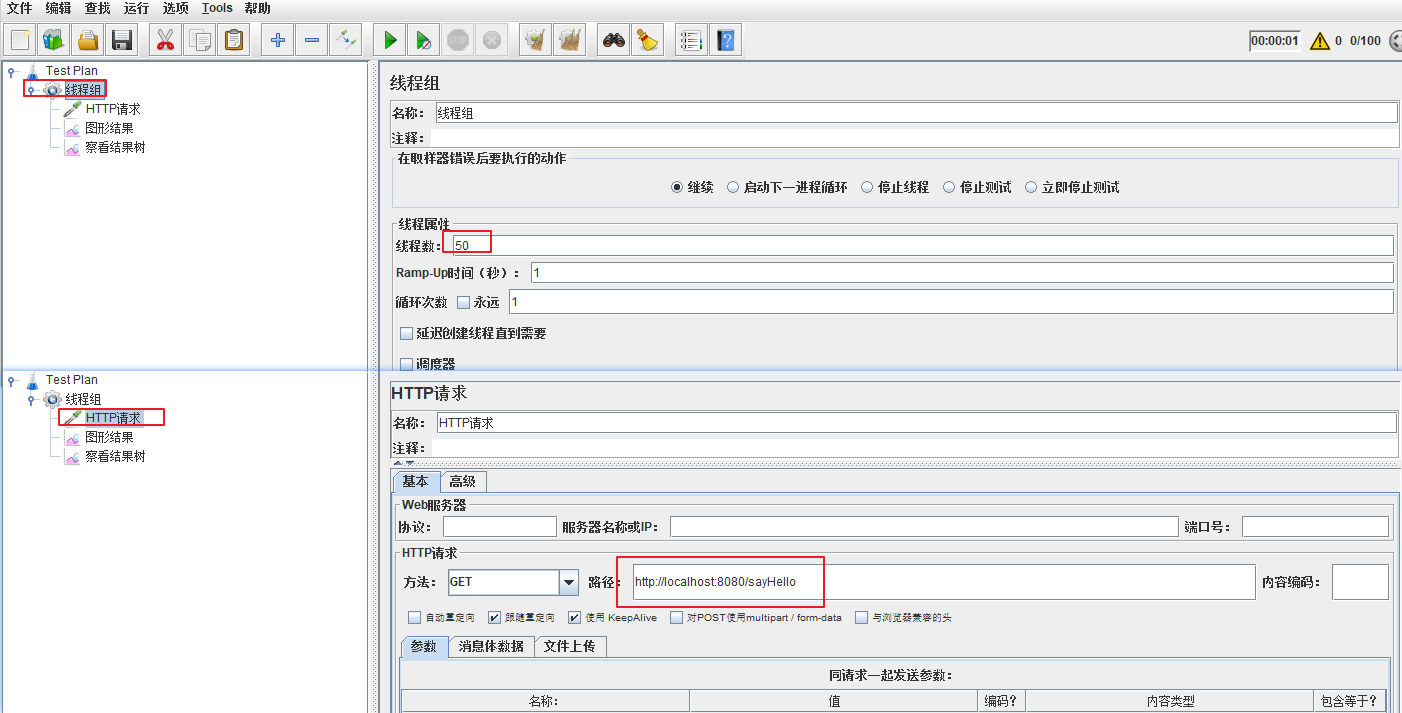

可以看到只有10个请求可以成功,其他失败;下一秒又有10个可以成功,失败的请求,控制台出现FlowException
参数说明
LimitApp
很多场景下,根据调用方来限流也是非常重要的。比如有两个服务 A 和 B 都向 Service Provider 发起调用请求,我们希望只对来自服务 B 的请求进行限流,则可以设置限流规则的 limitApp 为服务 B 的名称。Sentinel Dubbo Adapter 会自动解析 Dubbo 消费者(调用方)的 application name 作为调用方名称(origin),在进行资源保护的时候都会带上调用方名称。若限流规则未配置调用方(default),则该限流规则对所有调用方生效。若限流规则配置了调用方则限流规则将仅对指定调用方生效。
注:Dubbo 默认通信不携带对端 application name 信息,因此需要开发者在调用端手动将 application name 置入 attachment 中,provider 端进行相应的解析。Sentinel Dubbo Adapter 实现了一个 Filter 用于自动从 consumer 端向 provider 端透传 application name。若调用端未引入 Sentinel Dubbo Adapter,又希望根据调用端限流,可以在调用端手动将 application name 置入 attachment 中,key 为 dubboApplication
演示流程
- 修改provider中限流规则:
flowRule.setLimitApp("sentinel-web"); - 在consumer工程中,做如下处理。其中一个通过attachment传递了一个消费者的 application.name,另一个没有传,通过jmeter工具进行测试
@GetMapping("/sayHello")
public String sayHello(){
// 隐式传参,设定 dubbo 的应用名
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment("dubboApplication","sentinel-web");
return sentinelService.sayHello("zhangsan");
}
@GetMapping("/sayHello2")
public String say2Hello(){
return sentinelService.sayHello("zhangsan");
}
ControlBehavior
如果被限流了,则采取的行为。(拒绝策略)
当 QPS 超过某个阈值的时候,则采取措施进行流量控制。流量控制的手段包括以下几种:直接拒绝、Warm Up、匀速排队。对应 FlowRule 中的 controlBehavior 字段
直接拒绝(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT)方式是默认的流量控制方式,当QPS超过任意规则的阈值后,新的请求就会被立即拒绝,拒绝方式为抛出FlowException。这种方式适用于对系统处理能力确切已知的情况下,比如通过压测确定了系统的准确水位时
Warm Up(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_WARM_UP)方式,即预热/冷启动方式,当系统长期处于低并发的情况下,流量突然增加到qps的最高峰值,可能会造成系统的瞬间流量过大把系统压垮。所以warm up,相当于处理请求的数量是缓慢增加,经过一段时间以后,到达系统处理请求个数的最大值
匀速排队(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_RATE_LIMITER)方式会严格控制请求通过的间隔时间,也即是让请求以均匀的速度通过,对应的是漏桶算法
它的原理是,以固定的间隔时间让请求通过。当请求过来的时候,如果当前请求距离上个通过的请求通过的时间间隔不小于预设值,则让当前请求通过;否则,计算当前请求的预期通过时间,如果该请求的预期通过时间小于规则预设的 timeout 时间,则该请求会等待直到预设时间到来通过;反之,则马上抛出阻塞异常。
可以设置一个最长排队等待时间: flowRule.setMaxQueueingTimeMs(5 * 1000); // 最长排队等待时间:5s
这种方式主要用于处理间隔性突发的流量,例如消息队列。想象一下这样的场景,在某一秒有大量的请求到来,而接下来的几秒则处于空闲状态,我们希望系统能够在接下来的空闲期间逐渐处理这些请求,而不是在第一秒直接拒绝多余的请求。
如何实现分布式限流
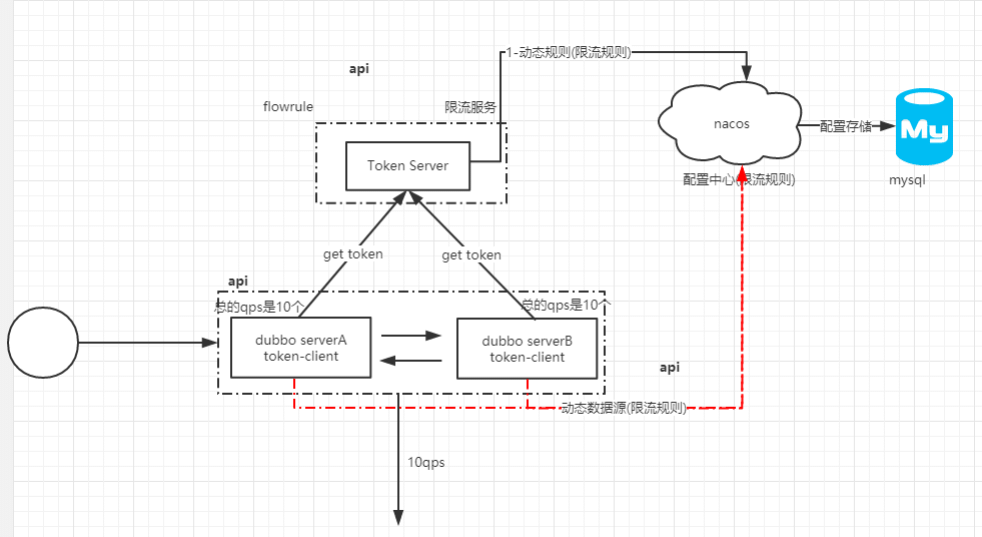
在前面的所有案例中,我们只是基于Sentinel的基本使用和单机限流的使用,假如有这样一个场景,我们现在把provider部署了10个集群,希望调用这个服务的api的总的qps是100,意味着每一台机器的 qps 是10,理想情况下总的qps就是100。但是实际上由于负载均衡策略的流量分发并不是非常均匀的,就会导致总的qps不足100时,就被限了。在这个场景中,仅仅依靠单机来实现总体流量的控制是有问题的。所以最好是能实现集群限流。
架构图
要想使用集群流控功能,我们需要在应用端配置动态规则源,并通过 Sentinel 控制台实时进行推送。如下图所示:
搭建token-server
Jar包依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-cluster-server-default</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-transport-simple-http</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
ClusterServer
public class ClusterServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClusterTokenServer tokenServer=new SentinelDefaultTokenServer();
ClusterServerConfigManager.loadGlobalTransportConfig(
new ServerTransportConfig().setIdleSeconds(600).setPort(9999));
ClusterServerConfigManager.
loadServerNamespaceSet(Collections.singleton("App-Mic"));
tokenServer.start();
}
}
DataSourceInitFunc
public class DataSourceInitFunc implements InitFunc {
private final String remoteAddress = "192.168.13.106"; //nacos远程服务host
private final String groupId = "SENTINEL_GROUP"; //nacos groupId
//namespace不同,限流规则也不同
private static final String FLOW_POSTFIX = "-flow-rules";
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
ClusterFlowRuleManager.setPropertySupplier(namespace -> {
ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> rds =
new NacosDataSource<>(
remoteAddress, groupId, namespace + FLOW_POSTFIX,
source -> JSON.parseObject(
source, new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>(){}));
return rds.getProperty();
});
}
}
resource目录添加扩展点
/META-INF/services/com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc = 自定义扩展点
添加log4j.properties文件
启动Sentinel dashboard
java -Dserver.port=8080 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8080 -
Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.6.1.jar
启动nacos以及增加配置
启动nacos服务: nohup sh startup.sh -m standalone &
增加限流配置
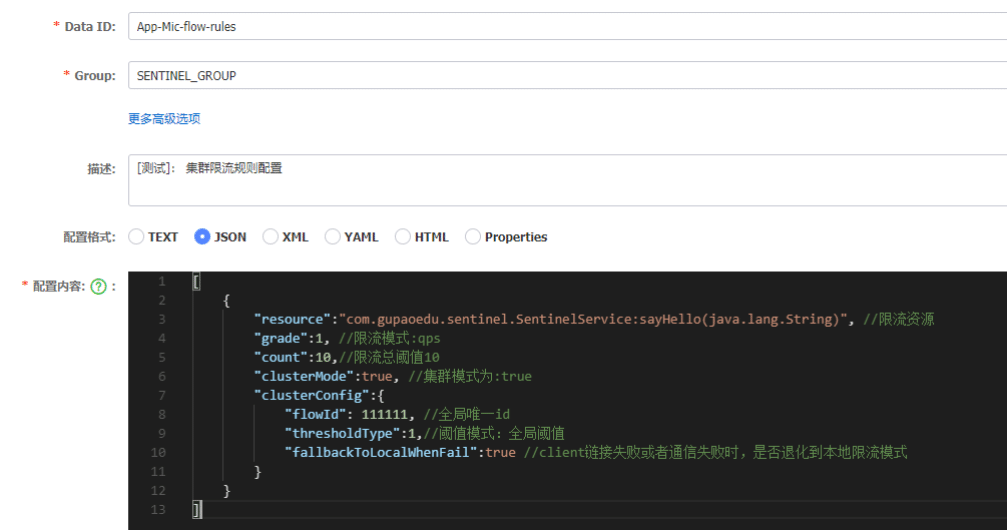
配置jvm参数
配置如下jvm启动参数,连接到sentinel dashboard
-Dproject.name=App-Mic -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=192.168.13.106:8080 -
Dcsp.sentinel.log.use.pid=true
服务启动之后,在 $user.home$/logs/csp/ 可以找到 sentinel-record.log.pid*.date 文件,如果看到日
志文件中获取到了远程服务的信息,说明token-server启动成功了
Dubbo接入分布式限流
在 sentinel-provider 中新增以下配置及类
jar包依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-dubbo-adapter</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-cluster-client-default</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-transport-simple-http</artifactId>
<version>1.6.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
增加扩展点
扩展点需要在 resources/META-INF/services/ 增加扩展的配置
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc = 自定义扩展点
public class DataSourceInitFunc implements InitFunc {
private static final String CLUSTER_SERVER_HOST = "localhost";//token-server的ip
private static final int CLUSTER_SERVER_PORT = 9999;//token-server 端口
private static final int REQUEST_TIME_OUT = 200000; //请求超时时间
private static final String APP_NAME = "App-Mic"; // namespace
private static final String REMOTE_ADDRESS = "192.168.13.106"; //nacos服务的ip
private static final String GROUP_ID = "SENTINEL_GROUP";//group id
private static final String FLOW_POSTFIX = "-flow-rules";//限流规则后缀
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
loadClusterClientConfig();
registerClusterFlowRuleProperty();
}
//通过硬编码的方式,配置连接到token-server服务的地址,{这种在实际使用过程中不建议,后续可以基于动态配置源改造}
public static void loadClusterClientConfig(){
ClusterClientAssignConfig assignConfig = new ClusterClientAssignConfig();
assignConfig.setServerHost(CLUSTER_SERVER_HOST);
assignConfig.setServerPort(CLUSTER_SERVER_PORT);
ClusterClientConfigManager.applyNewAssignConfig(assignConfig);
ClusterClientConfig clientConfig = new ClusterClientConfig();
//token-client请求 token-server获取令牌的超时时间
clientConfig.setRequestTimeout(REQUEST_TIME_OUT);
ClusterClientConfigManager.applyNewConfig(clientConfig);
}
/**
* 注册动态规则Property
* 当client与Server连接中断,退化为本地限流时需要用到的该规则
* 该配置为必选项,客户端会从nacos上加载限流规则,请求tokenserver时,会戴上要check的规则id
* {这里的动态数据源,我们稍后会专门讲到}
*/
private static void registerClusterFlowRuleProperty(){
// 使用 Nacos 数据源作为配置中心,需要在 REMOTE_ADDRESS 上启动一个 Nacos 的服务
ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> ds = new
NacosDataSource<List<FlowRule>>(
REMOTE_ADDRESS, GROUP_ID, APP_NAME+FLOW_POSTFIX,
source -> JSON.parseObject(
source, new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {}));
// 为集群客户端注册动态规则源
FlowRuleManager.register2Property(ds.getProperty());
}
指定客户端
SentinelProviderApplication
@SpringBootApplication
public class SentinelProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//表示当前的节点是集群客户端
ClusterStateManager.applyState(ClusterStateManager.CLUSTER_CLIENT);
SpringApplication.run(SentinelProviderApplication.class, args);
System.in.read();
}
}
配置jvm参数
这里的project-name要包含在token-server中配置的namespace中,
token server 会根据客户端对应的 namespace(默认为 project.name 定义的应用名)下的连接数来计算总的阈值
-Dproject.name=App-Mic -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=192.168.8.106:8080 -
Dcsp.sentinel.log.use.pid=true
服务启动之后,在 $user.home$/logs/csp/ 可以找到 sentinel-record.log.pid*.date 文件,如果看到日
志文件中获取到了token-server的信息,说明连接成功了
演示集群限流
所谓集群限流,就是多个服务节点使用同一个限流规则。从而对多个节点的总流量进行限制,添加一个sentinel-server。同时运行两个程序
压测
使用jmeter创建1000个线程,进行压测,然后关注sentinel dashboard的变化。
Sentinel 熔断
场景分析
在大型分布式架构中,一个用户的请求,可能是这样
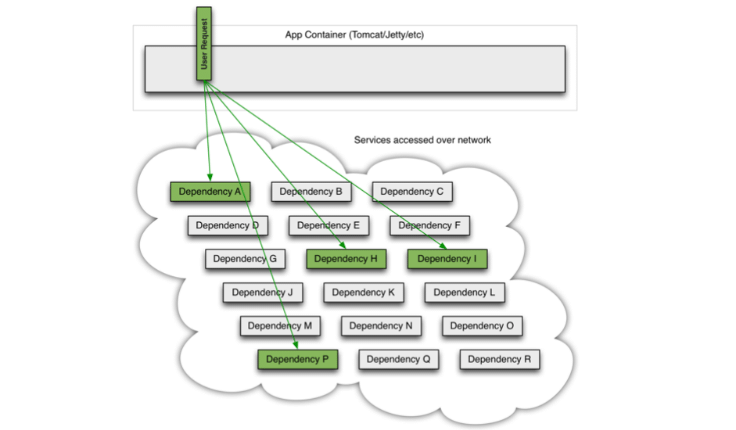
如果这个时候一个服务出现异常
- 服务提供者不可用(硬件故障、程序bug、网络故障、用户请求量较大)
- 重试导致的流量过大
- 服务调用者使用同步调用,产生大量的等待线程占用系统资源,一旦线程资源被耗尽,调用者提供的服务也会变成不可用状态
就会导致请求堆集从而出现整个服务不可用的问题。用古话来讲就是:千里之堤毁于蚁穴
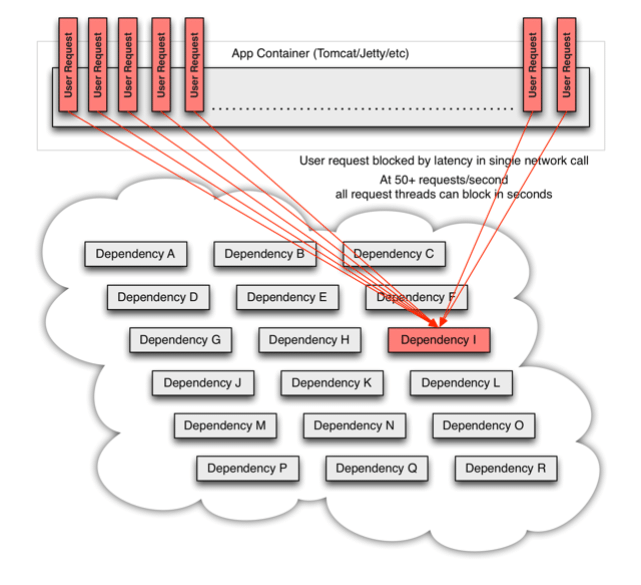
在复杂的分布式架构的应用程序有很多的依赖,都会不可避免的出现服务故障等问题。高并发的依赖失败时如果没有隔离措施,当前应用服务就有被拖垮的风险。
引入熔断机制
在分布式架构中,有一种解决方法,就是熔断机制。
也就是说当下游服务因为访问压力过大或者其他原因导致响应变慢的时候,上游服务为了保护自己以及系统整体的可用性,可以暂时切断对于下游服务的调用。
熔断在生活中也随处可见,
- 比如 “跳闸”,当电压超过负荷时,开关会自动跳闸。从而防止出现电路烧毁带来的火灾。
- 比如股票市场的熔断,对于股票设置一个熔断价格,当价格触发到熔断点之后,交易会被暂停一段时间。或者交易可以继续进行,但是报价会限制在一定的范围
那生活中的这种场景,能不能应用在架构设计中呢?
思考熔断机制的实现设计
那么大家在思考一下,如过项目中要实现熔断,是不是也需要像股票或者电闸这种设计一样,需要设置一个阈值呢?
大家会发现,架构是基于人的架构,所以架构的设计都是基于人对于事务的基本认识来实施的。因此越往后面学习,越能够发现很多设计思想都来自于生活。
Sentinel熔断降级
Sentinel 熔断降级会在调用链路中某个资源出现不稳定状态时(例如调用超时或异常比例升高),对这个资源的调用进行限制,让请求快速失败,避免影响到其它的资源而导致级联错误。当资源被降级后,在接下来的降级时间窗口之内,对该资源的调用都自动熔断。
那么怎么去判断资源是否处于稳定状态呢?
- 平均响应时间,比如,在1s内连续处理5个请求,它的平均响应时间都超过阈值,那么在后续的时间窗口中,对于这个方法的调用都会自动熔断,sentinel默认的平均响应时间是4900ms
- 异常比例,当指定资源每秒请求量大于等于5,并且每秒的异常总数占通过量的比值超过阈值之后(比如每秒处理1000个请求,那么其中异常请求数为500,那么当前的比值是50%),那么该资源会进入降级状态。异常的比率范围是[0.0.1.0]表示0%到100%
- 异常数,当资源在1分钟的异常数据超过阈值后会进行熔断
针对这些规则,Sentinel中给出了响应的字段来设置
| Field | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| resource | 资源名,即限流规则的作用对象 | |
| count | 阈值 | |
| grade | 降级模式,根据 RT 降级还是根据异常比例降级 | RT |
| timeWindow | 降级的时间,单位为 s |
平均响应时间 (DEGRADE_GRADE_RT):当 1s 内持续进入 5 个请求,对应时刻的平均响应时间(秒级)均超过阈值(count,以 ms 为单位),那么在接下的时间窗口(DegradeRule 中的 timeWindow,以 s 为单位)之内,对这个方法的调用都会自动地熔断(抛出 DegradeException)。
注意 Sentinel 默认统计的 RT 上限是 4900 ms,超出此阈值的都会算作 4900 ms,若需要变更此上限
可以通过启动配置项 -Dcsp.sentinel.statistic.max.rt=xxx 来配置。
异常比例 (DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO):当资源的每秒请求量 >= 5,并且每秒异常总数占通过量的比值超过阈值(DegradeRule 中的 count)之后,资源进入降级状态,即在接下的时间窗口(DegradeRule 中的 timeWindow,以 s 为单位)之内,对这个方法的调用都会自动地返回。异常比率的阈值范围是 [0.0, 1.0],代表 0% - 100%。
异常数 (DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_COUNT):当资源近 1 分钟的异常数目超过阈值之后会进行熔断。注意由于统计时间窗口是分钟级别的,若 timeWindow 小于 60s,则结束熔断状态后仍可能再进入熔断状态。
熔断演示
Jar包依赖
在这个案例中,我们可以基于前面讲解的dubbo服务进行改造,只需要依赖这个jar,
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-dubbo-adapter</artifactId>
<version>1.6.2</version>
</dependency>
配置规则
添加一个DegradeInitFunc。
resource/META-INF/services/com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc 中配置改类的全路径,这样的话sentinel在触发限流时会去调用这个initFunc来解析规则
com.gupao.sentinel.sentinelprovider.DegradeInitFunc
public class DegradeInitFunc implements InitFunc {
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
List<DegradeRule> rules=new ArrayList<>();
DegradeRule rule=new DegradeRule();
//下面这个配置的意思是,当1s内持续进入5个请求,平均响应时间都超过count(10ms),
// 那么在接下来的timewindow(10s)内,对
//这个方法的调用都会自动熔断,抛出异常:degradeException.
//指定被保护的资源
rule.setResource("com.gupaoedu.sentinel.SentinelService");
rule.setCount(10); //阈值
//降级模式, RT(平均响应时间)、异常比例(DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO)/异常数量
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_RT);
rule.setTimeWindow(10);//降级的时间单位, 单位为s
rules.add(rule);
DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
}
修改SentinelServiceImpl
增加一个sleep,这个时候就会起到一个熔断的效果
@Override
public String sayHello(String msg) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500); //添加这个和不添加这个的影响
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("begin execute sayHello:"+name);
return "hello " + msg;
}
被降级之后可以在控制台看到 DegradeException
