sentinel限流熔断的应用及原理
常见的限流方式
semphore
Semaphore 是 jdk 提供的方式。Semaphore(信号量),用于做限流处理,比如说同时只允许5五个人访问,超过五个人访问就需要等待,类似这样的需求,下面的案例可以看出是五个五个的执行,等上一个五个执行完了,才会执行下一个
public class SemphoreDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程池
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 只能5个线程同时访问
final Semaphore semp = new Semaphore(5);
// 模拟20个客户端访问
for (int index = 0; index < 20; index++) {
final int NO = index;
exec.execute(() -> {
// 获取许可
try {
semp.acquire();
System.out.println("Accessing: " + NO);
//模拟实际业务逻辑
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 10000));
// 访问完后,释放
semp.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 退出线程池
exec.shutdown();
}
}
RateLimiter
Guava(RateLimiter) -> 令牌桶/漏桶
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>20.0</version>
</dependency>
public class RateLimiterDemo {
static RateLimiter rateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(5);
private static void getAcquire(int index) {
if (rateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
System.out.println(index + "允许进行访问!");
}else{
System.out.println(index + "被限流了!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
final int index = i;
new Thread(()->{
try {
latch.await();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(1000));
getAcquire(index);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
latch.countDown();
}
}
RRateLimiter
Redisson(RRateLimiter)(令牌桶)
redis 的分布式限流方式 oschina
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
@Slf4j
public class RedissonDemo {
private final RedissonClient redisClient;
private final String key = "msgRateLimiter:" + "test";
private final int limiter = 10000;
@Autowired
public RedissonDemo(RedissonClient redisClient) {
this.redisClient = redisClient;
}
//服务启动的时候,先清一下 redis,防止 count 出错
public void reload() {
RMapCache<String, Integer> msgRateLimit =
redisClient.getMapCache(key, IntegerCodec.INSTANCE);
if (msgRateLimit.containsKey(key)) {
msgRateLimit.delete();
}
}
//该方法可以配合 mq,结果是 true 的话就 ack,false 的话就 reject
public boolean handleMessage() {
//分布式场景下的限流
//String key = "msgRateLimiter:" + MsgConstants.MsgType.APP_PUSH[0];
RMapCache<String, Integer> msgRateLimit =
redisClient.getMapCache(key, IntegerCodec.INSTANCE);
Integer count;
try {
msgRateLimit.putIfAbsent(key, 0, 1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
count = msgRateLimit.addAndGet(key, 1);
log.info("get redis counter:{}", count);
if (count < limiter) {
//此处是你要执行的代码
return true;
}
log.warn("超过限流:{}", count);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("err", e);
}
return false;
}
}
Alibaba Sentinel
什么是 Sentinel
Sentinel:分布式系统的流量防卫兵
随着微服务的流行,服务和服务之间的稳定性变得越来越重要。Sentinel 以流量为切入点,从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度保护服务的稳定性。
Sentinel 分为两个部分:
- 核心库(Java 客户端)不依赖任何框架/库,能够运行于所有 Java 运行时环境,同时对 Dubbo / Spring Cloud 等框架也有较好的支持。
- 控制台(Dashboard)基于 Spring Boot 开发,打包后可以直接运行,不需要额外的 Tomcat 等应用容器。
Sentinel 具有以下特征:
- 丰富的应用场景:Sentinel 承接了阿里巴巴近 10 年的双十一大促流量的核心场景,例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系统容量可以承受的范围)、消息削峰填谷、集群流量控制、实时熔断下游不可用应用等。
- 完备的实时监控:Sentinel 同时提供实时的监控功能。您可以在控制台中看到接入应用的单台机器秒级数据,甚至 500 台以下规模的集群的汇总运行情况。
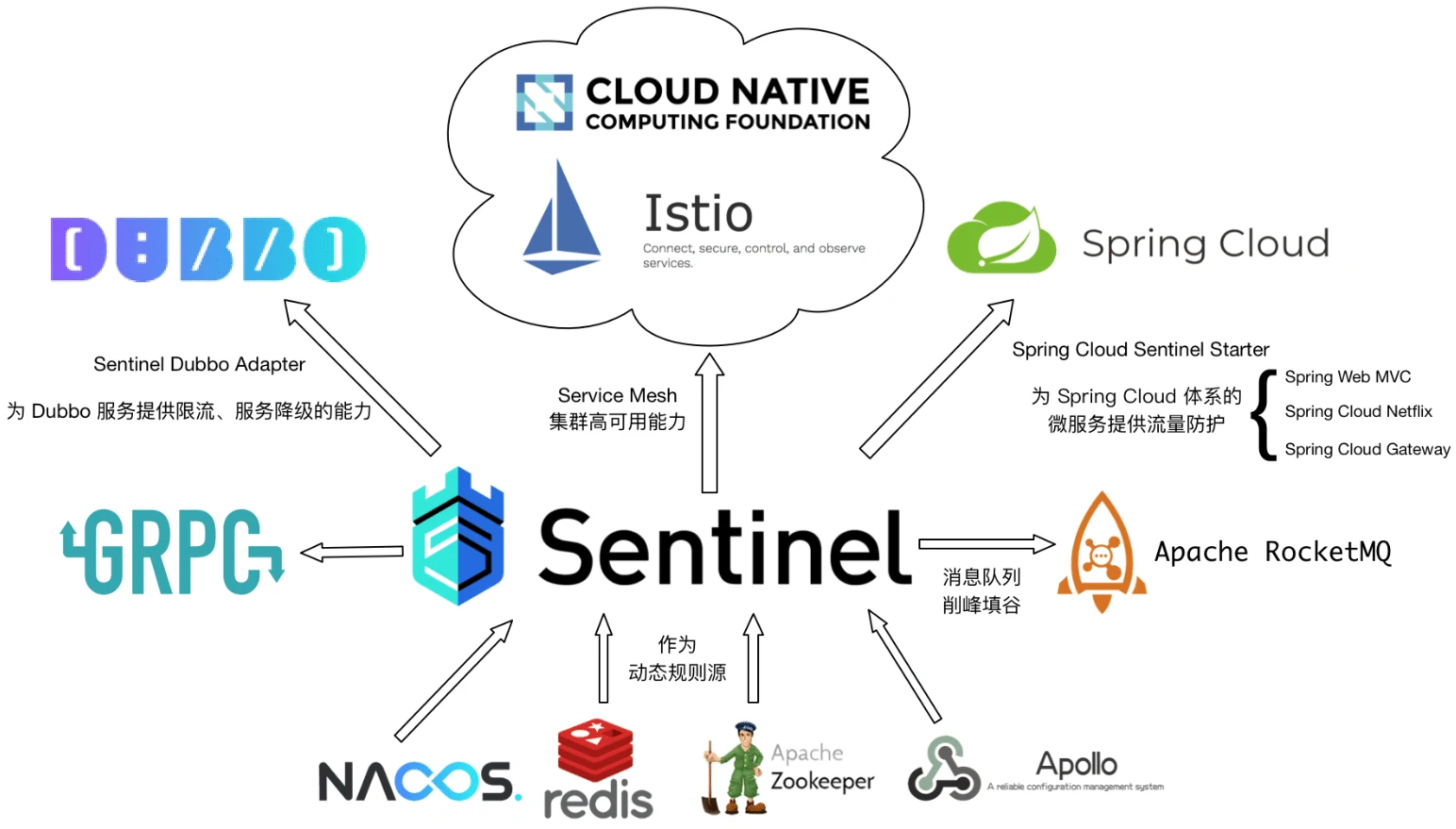
- 广泛的开源生态:Sentinel 提供开箱即用的与其它开源框架/库的整合模块,例如与 Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC 的整合。您只需要引入相应的依赖并进行简单的配置即可快速地接入 Sentinel。
- 完善的 SPI 扩展点:Sentinel 提供简单易用、完善的 SPI 扩展接口。您可以通过实现扩展接口来快速地定制逻辑。例如定制规则管理、适配动态数据源等。
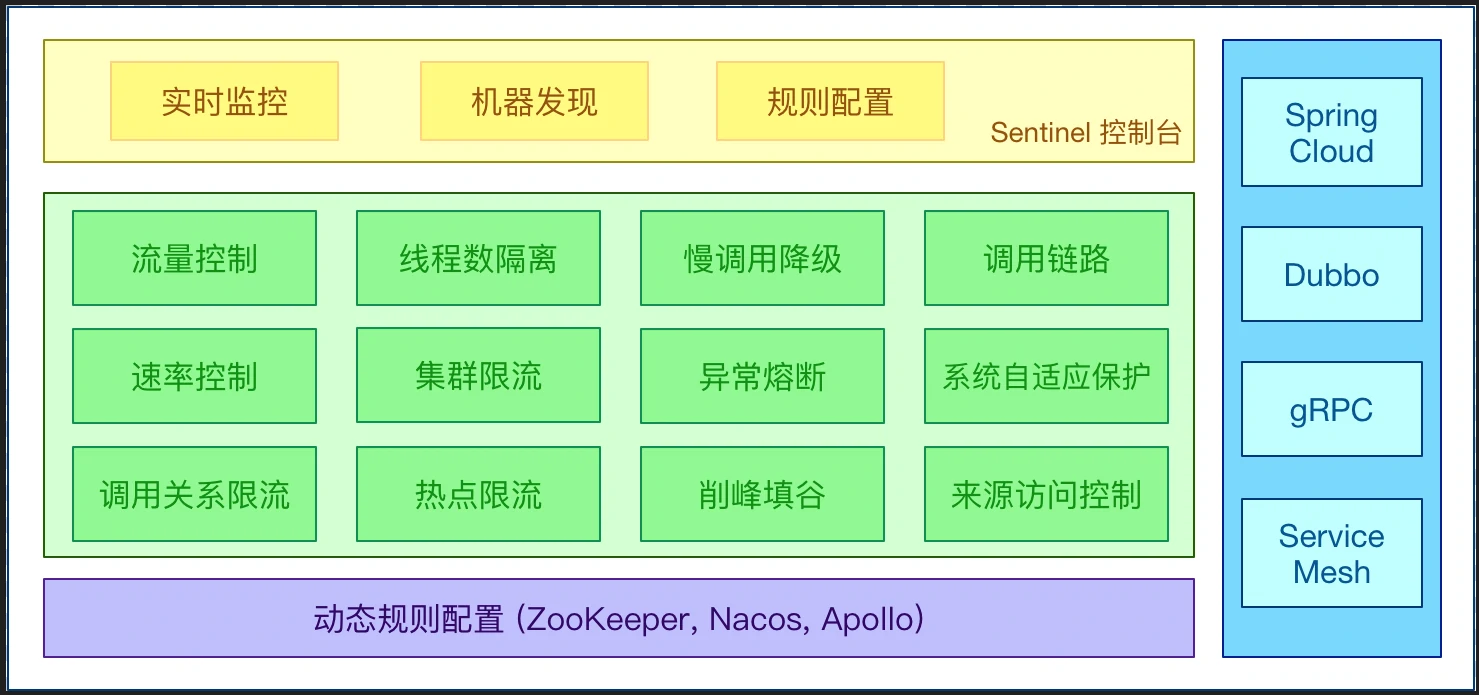
Sentinel 特点
Sentinel 的主要特性:
Sentinel 的开源生态:
Sentinel 使用
- 初始化限流规则
- 根据限流规则进行限流
pom 依赖
<!--sentinel 核心类库-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--sentinel 集成到控制台使用的http组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-transport-simple-http</artifactId>
<version>1.6.3</version>
</dependency>
测试类 SentinelDemo:
public class SentinelDemo {
private static String resource = "test sentinel";
private static void initFlowRule() {
// 限流规则的集合
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
FlowRule flowRule = new FlowRule();
// 资源(方法名称、接口)
flowRule.setResource(resource);
// 限流阈值类型(qps、线程数)
flowRule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
// 限流10个
flowRule.setCount(10);
rules.add(flowRule);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化限流规则
initFlowRule();
while (true) {
Entry entry = null;
try {
// 根据限流规则进行限流
entry = SphU.entry(resource);
System.out.println("可以进行访问");
} catch (BlockException e) { //如果被限流了,那么会抛出这个异常
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (null != entry) {
entry.exit();// 释放
}
}
}
}
}
启动 sentinel 控制台 dashaboard,在 github 上下载 sentinel-dashboard-1.6.3.jar
使用如下命令在命令行中启动 jar 包
# Dserver.port=8888,表示使用8888端口启动服务
# Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8888,表示把当前dashboard也加入限流监控
# Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard,设置当前dashboard应用名称为 sentinel-dashboard
java -jar -Dserver.port=8888 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8888 -Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard .\sentinel-dashboard-1.6.3.jar

可以通过浏览器访问,http://localhost:8888,账号/密码:sentinel/sentinel,显示如下界面:

然后启动 SentinelDemo,并加入限流监控,配置监控地址和应用名称,并启动

然后可以在 dashboard 看到 SentinelDemo 的界面

Sentinel限流的思考
- 限流用了什么算法来实现的?(滑动窗口)
- 它是怎么实现的?(责任链有关系)
- SPI的扩展
sentinel 源码分析
调用关系
SphU.entry->Env.sph.entry->entry->entryWithPriority->lookProcessChain->chain.entry
lookProcessChain
ProcessorSlot<Object> lookProcessChain(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) {
ProcessorSlotChain chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
if (chain == null) {
synchronized (LOCK) {
chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
if (chain == null) {
// Entry size limit.
if (chainMap.size() >= Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE) {
return null;
}
chain = SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain();
Map<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain> newMap =
new HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain>(
chainMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(chainMap);
newMap.put(resourceWrapper, chain);
chainMap = newMap;
}
}
}
return chain;
}
SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain
public static ProcessorSlotChain newSlotChain() {
if (builder != null) {
return builder.build();
}
resolveSlotChainBuilder();
if (builder == null) {
RecordLog.warn("[SlotChainProvider] Wrong state when resolving slot chain builder, using default");
builder = new DefaultSlotChainBuilder();
}
return builder.build();
}
builder.build
@Override
public ProcessorSlotChain build() {
ProcessorSlotChain chain = new DefaultProcessorSlotChain();
chain.addLast(new NodeSelectorSlot());
chain.addLast(new ClusterBuilderSlot());
chain.addLast(new LogSlot());
chain.addLast(new StatisticSlot());
chain.addLast(new SystemSlot());
chain.addLast(new AuthoritySlot());
chain.addLast(new FlowSlot());
chain.addLast(new DegradeSlot());
return chain;
}
sentinel 架构
在 Sentinel 里面,所有的资源都对应一个资源名称(resourceName),每次资源调用都会创建一个 Entry 对象。Entry 可以通过对主流框架的适配自动创建,也可以通过注解的方式或调用 SphU API 显式创建。Entry 创建的时候,同时也会创建一系列功能插槽(slot chain),这些插槽有不同的职责,例如:
NodeSelectorSlot: 负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级;ClusterBuilderSlot: 则用于存储资源的统计信息以及调用者信息,例如该资源的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,这些信息将用作为多维度限流,降级的依据;StatisticSlot: 则用于记录、统计不同纬度的 runtime 指标监控信息;FlowSlot: 则用于根据预设的限流规则以及前面 slot 统计的状态,来进行流量控制;AuthoritySlot: 则根据配置的黑白名单和调用来源信息,来做黑白名单控制;DegradeSlot: 则通过统计信息以及预设的规则,来做熔断降级;SystemSlot: 则通过系统的状态,例如 load1 等,来控制总的入口流量;
总体的框架如下:
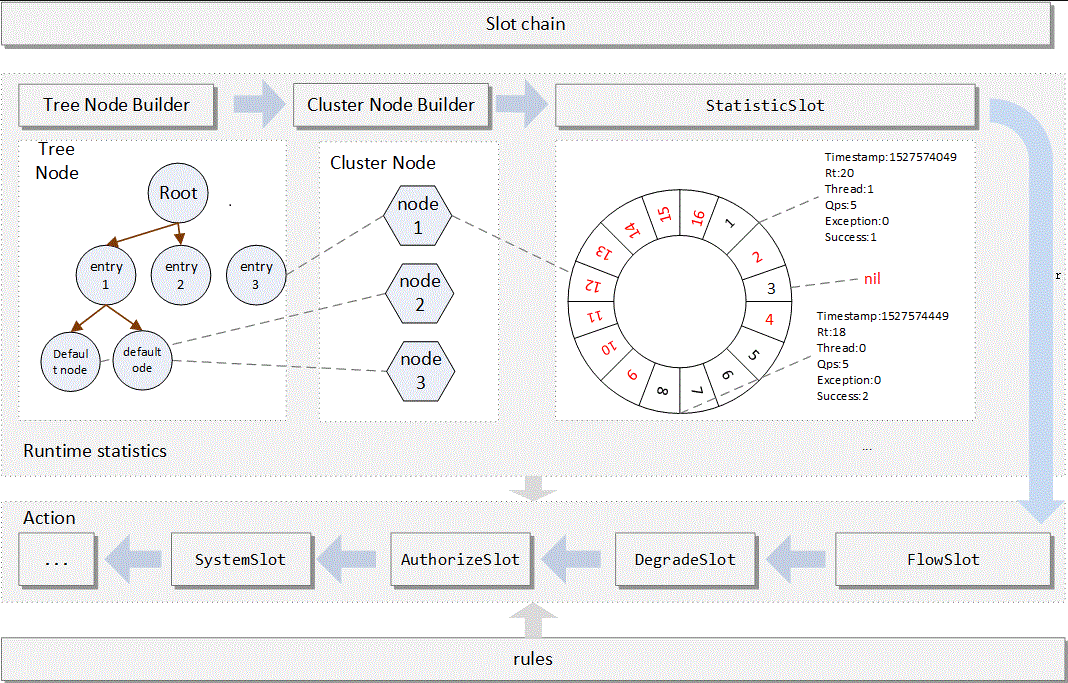
Sentinel 将 SlotChainBuilder 作为 SPI 接口进行扩展,使得 Slot Chain 具备了扩展的能力。您可以自行加入自定义的 slot 并编排 slot 间的顺序,从而可以给 Sentinel 添加自定义的功能。
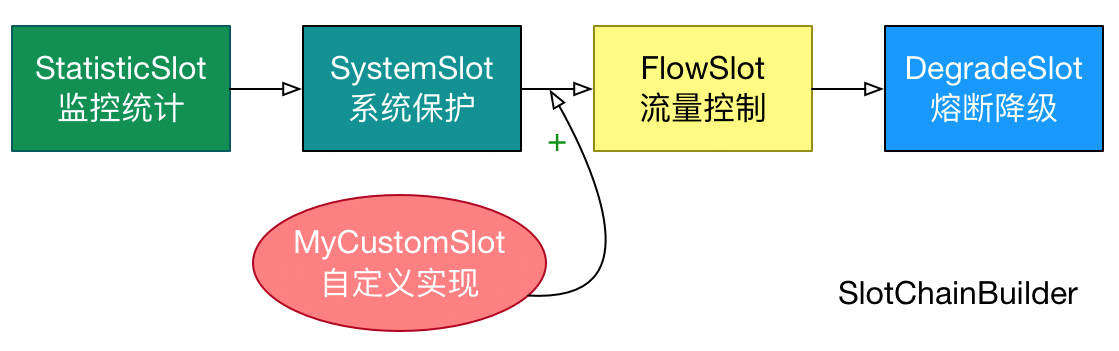
滑动窗口算法实现
在 sentinel 调用链中 StatisticSlot 负责数据的统计,所以会涉及到限流规则中设置的数量。
StatisticSlot.entry
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
try {
// Do some checking.
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
// Request passed, add thread count and pass count.
node.increaseThreadNum();
node.addPassRequest(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
// Add count for origin node.
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().addPassRequest(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.addPassRequest(count);
}
// Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
} catch (PriorityWaitException ex) {
// ...
} catch (BlockException e) {
// Blocked, set block exception to current entry.
// ...
} catch (Throwable e) {
// Unexpected error, set error to current entry.
// ...
}
}
node.addPassRequest
@Override
public void addPassRequest(int count) {
super.addPassRequest(count);
this.clusterNode.addPassRequest(count);
}
clusterNode.addPassRequest
@Override
public void addPassRequest(int count) {
rollingCounterInSecond.addPass(count);
rollingCounterInMinute.addPass(count);
}
rollingCounterInMinute.addPass
@Override
public void addPass(int count) {
// 获取当前窗口
WindowWrap<MetricBucket> wrap = data.currentWindow();
// 计数
wrap.value().addPass(count);
}
data.currentWindow
data.currentWindow -> data.currentWindow
public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) {
if (timeMillis < 0) {
return null;
}
// 获取当前时间所在窗口的索引
int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis);
// 获取当前时间所在窗口开始时间
// Calculate current bucket start time.
long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis);
/*
* Get bucket item at given time from the array.
*
* (1) Bucket is absent, then just create a new bucket and CAS update to circular array.
* (2) Bucket is up-to-date, then just return the bucket.
* (3) Bucket is deprecated, then reset current bucket and clean all deprecated buckets.
*/
while (true) {
WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx);
if (old == null) {
/*
* B0 B1 B2 NULL B4
* ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp
* ^
* time=888
* bucket is empty, so create new and update
*
* If the old bucket is absent, then we create a new bucket at {@code windowStart},
* then try to update circular array via a CAS operation. Only one thread can
* succeed to update, while other threads yield its time slice.
*/
WindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) {
// Successfully updated, return the created bucket.
return window;
} else {
// Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available.
Thread.yield();
}
} else if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) {
/*
* B0 B1 B2 B3 B4
* ||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 timestamp
* ^
* time=888
* startTime of Bucket 3: 800, so it's up-to-date
*
* If current {@code windowStart} is equal to the start timestamp of old bucket,
* that means the time is within the bucket, so directly return the bucket.
*/
return old;
} else if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) {
/*
* (old)
* B0 B1 B2 NULL B4
* |_______||_______|_______|_______|_______|_______||___
* ... 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 timestamp
* ^
* time=1676
* startTime of Bucket 2: 400, deprecated, should be reset
*
* If the start timestamp of old bucket is behind provided time, that means
* the bucket is deprecated. We have to reset the bucket to current {@code windowStart}.
* Note that the reset and clean-up operations are hard to be atomic,
* so we need a update lock to guarantee the correctness of bucket update.
*
* The update lock is conditional (tiny scope) and will take effect only when
* bucket is deprecated, so in most cases it won't lead to performance loss.
*/
if (updateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
// Successfully get the update lock, now we reset the bucket.
return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart);
} finally {
updateLock.unlock();
}
} else {
// Contention failed, the thread will yield its time slice to wait for bucket available.
Thread.yield();
}
} else if (windowStart < old.windowStart()) {
// Should not go through here, as the provided time is already behind.
return new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
}
}
}
数量计算完毕之后会调用 FlowSlot 的 entry 方法校验规则
FlowSlot#entry
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
checkFlow(resourceWrapper, context, node, count, prioritized);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
checkFlow
public void checkFlow(Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider, ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException {
if (ruleProvider == null || resource == null) {
return;
}
Collection<FlowRule> rules = ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName());
if (rules != null) {
for (FlowRule rule : rules) {
if (!canPassCheck(rule, context, node, count, prioritized)) {
throw new FlowException(rule.getLimitApp(), rule);
}
}
}
}