设计模式-代理模式
代理模式
代理模式的应用场景
在生活中,我们经常见到这样的场景,如:租房中介、售票黄牛、婚介、经纪人、快递、事务代理、非侵入式日志监听等,这些都是代理模式的实际体现。代理模式(Proxy Pattern)的定义也非常简单,是指为其他对象提供一种代理,以控制对这个对象的访问。
代理对象在客服端和目标对象之间起到中介作用,代理模式属于结构型设计模式。使用代理模式主要有两个目的:一保护目标对象,二增强目标对象。下面我们来看一下代理模式的类结构图:
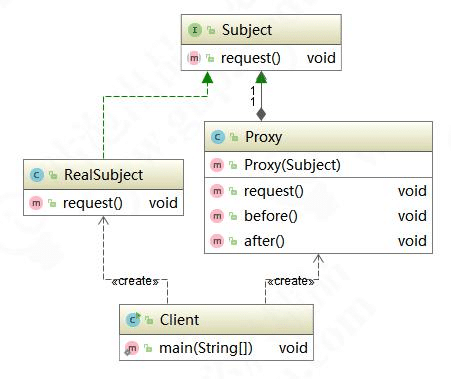
Subject 是顶层接口,RealSubject 是真实对象(被代理对象),Proxy 是代理对象,代理对象持有被代理对象的引用,客户端调用代理对象方法,同时也调用被代理对象的方法,但是在代理对象前后增加一些处理。在代码中,我们想到代理,就会理解为是代码增强,其实就是在原本逻辑前后增加一些逻辑,而调用者无感知。代理模式属于结构型模式,有静态代理和动态代理。
静态代理
举个例子:人到了适婚年龄,父母总是迫不及待希望早点抱孙子。而现在社会的人在各种压力之下,都选择晚婚晚育。于是着急的父母就开始到处为自己的子女相亲,比子女自己还着急。这个相亲的过程,就是一种我们人人都有份的代理。来看代码实现:
顶层接口 Person:
/**
*人有很多行为,要谈恋爱,要住房子,要购物,要工作
*/
public interface Person {
public void findLove();
}
儿子 Son 要找对象,实现 Person 类:
public class Son implements Person{
public void findLove(){
//我没有时间
//工作忙
System.out.println("儿子要求:肤白貌美大长腿");
}
}
父亲要帮儿子相亲,实现 Father 类:
public class Father {
private Son son;
//没办法扩展
public Father(Son son){
this.son = son;
}
//目标对象的引用给拿到
public void findLove(){
System.out.println("父母物色对象");
this.son.findLove();
System.out.println("双方同意交往,确立关系");
}
}
来看测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//只能帮儿子找对象
//不能帮表妹、不能帮陌生人
Father father = new Father(new Son());
father.findLove();
}
运行结果:

这里小伙伴们可能会觉得还是不知道如何讲代理模式应用到业务场景中,那么我们再来举例一个实际的业务场景。在分布式业务场景中,我们通常会对数据库进行分库分表,分库分表之后使用 Java 操作时,就可能需要配置多个数据源,我们通过设置数据源路由来动态切换数据源。先创建 Order 订单实体:
public class Order {
private Object orderInfo;
private Long createTime;
private String id;
public Object getOrderInfo() {
return orderInfo;
}
public void setOrderInfo(Object orderInfo) {
this.orderInfo = orderInfo;
}
public Long getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Long createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
创建 OrderDao 持久层操作类:
public class OrderDao {
public int insert(Order order){
System.out.println("OrderDao 创建 Order 成功!");
return 1;
}
}
创建 IOrderService 接口:
public interface IOrderService {
int createOrder(Order order);
}
创建 OrderService 实现类:
public class OrderService implements IOrderService {
private OrderDao orderDao;
public OrderService(){
//如果使用 Spring 应该是自动注入的
//这里为了使用方便,在构造方法中将 orderDao 直接初始化了
orderDao = new OrderDao();
}
@Override
public int createOrder(Order order) {
System.out.println("OrderService 调用 orderDao 创建订单");
return orderDao.insert(order);
}
}
接下来使用静态代理,主要完成的功能是,根据订单创建时间自动按年进行分库。根据开闭原则,原来写好的逻辑我们不去修改,通过代理对象来完成。先创建数据源路由对象,我们使用 ThreadLocal 的单例实现,DynamicDataSourceEntry 类:
/**
* 动态切换数据源
*/
public class DynamicDataSourceEntry {
// 默认数据源
public final static String DEFAULT_SOURCE = null;
private final static ThreadLocal<String> local = new ThreadLocal<String>();
private DynamicDataSourceEntry() {
}
/**
* 清空数据源
*/
public static void clear() {
local.remove();
}
/**
* 获取当前正在使用的数据源名字
*
* @return String
*/
public static String get() {
return local.get();
}
/**
* 还原当前切面的数据源
*/
public static void restore() {
local.set(DEFAULT_SOURCE);
}
/**
* 设置已知名字的数据源
*
* @param source
*/
public static void set(String source) {
local.set(source);
}
/**
* 根据年份动态设置数据源
*
* @param year
*/
public static void set(int year) {
local.set("DB_" + year);
}
}
创建切换数据源的代理 OrderServiceSaticProxy 类:
public class OrderServiceStaticProxy implements IOrderService {
private SimpleDateFormat yearFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy");
private IOrderService orderService;
public OrderServiceStaticProxy(IOrderService orderService){
this.orderService = orderService;
}
public int createOrder(Order order) {
before();
Long time = order.getCreateTime();
Integer dbRouter = Integer.valueOf(yearFormat.format(new Date(time)));
System.out.println("静态代理类自动分配到【DB_" + dbRouter + "】数据源处理数据。");
DynamicDataSourceEntry.set(dbRouter);
orderService.createOrder(order);
after();
return 0;
}
private void before(){
System.out.println("Proxy before method.");
}
private void after(){
System.out.println("Proxy after method.");
}
}
来看测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Order order = new Order();
// Date today = new Date();
// order.setCreateTime(today.getTime());
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Date date = sdf.parse("2017/02/01");
order.setCreateTime(date.getTime());
IOrderService orderService = new OrderServiceStaticProxy(new OrderService());
orderService.createOrder(order);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();;
}
}
运行效果:
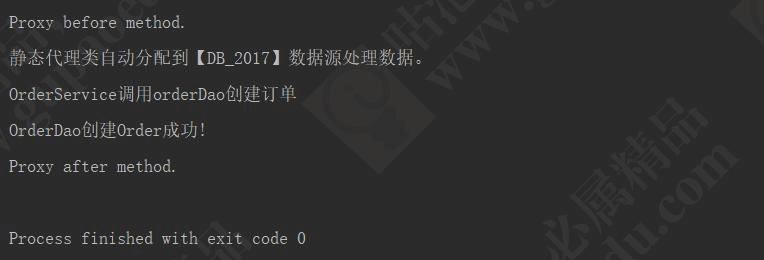
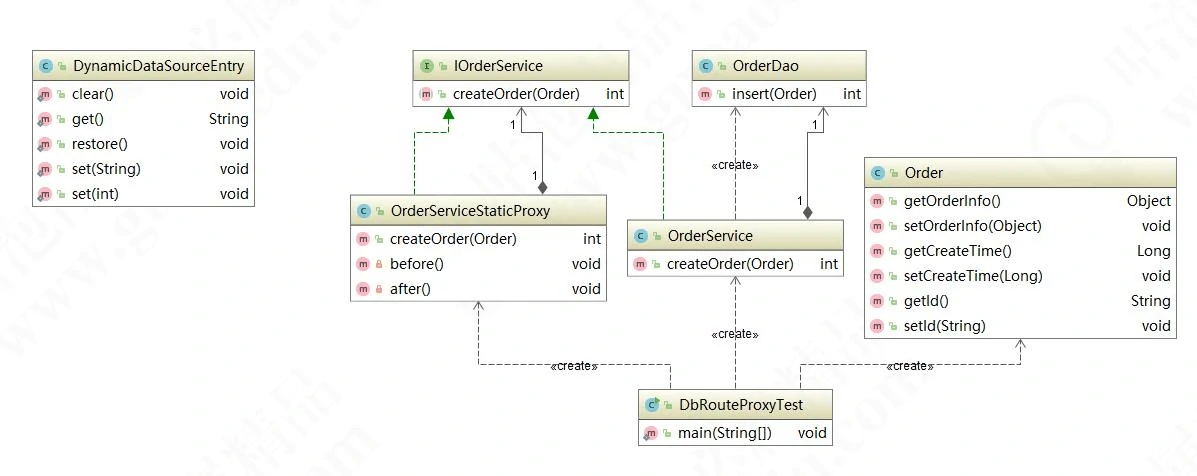
符合我们的预期效果。现在我们再来回顾一下类图,看是不是和我们最先画的类结构一致:
动态代理
动态代理和静态对比基本思路是一致的,只不过动态代理功能更加强大,随着业务的扩展适应性更强。如果还以找对象为例,使用动态代理相当于是能够适应复杂的业务场景。
不仅仅只是父亲给儿子找对象,如果找对象这项业务发展成了一个产业,进而出现了媒婆、婚介所等这样的形式。那么,此时用静态代理成本就更大了,需要一个更加通用的解决方案,要满足任何单身人士找对象的需求。我们升级一下代码,先来看 JDK 实现方式:
JDK 动态代理
创建媒婆(婚介)JDKMeipo 类:
public class JDKMeipo implements InvocationHandler{
//被代理的对象,把引用给保存下来
private Object target;
public Object getInstance(Object target) throws Exception{
this.target = target;
Class<?> clazz = target.getClass();
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(clazz.getClassLoader(),
clazz.getInterfaces(), this);
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)throws Throwable{
before();
Object obj = method.invoke(this.target,args);
after();
return obj;
}
private void before(){
System.out.println("我是媒婆:我要给你找对象,现在已经拿到你的需求");
System.out.println("开始物色");
}
private void after(){
System.out.println("如果合适的话,就准备办事");
}
}
创建单身客户 Customer 类:
public class Customer implements Person{
public void findLove(){
System.out.println("高富帅");
System.out.println("身高 180cm");
System.out.println("胸大,6块腹肌");
}
}
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Person obj = (Person)new JDKMeipo().getInstance(new Customer());
obj.findLove();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
运行效果:

上面的案例理解了话,我们再来看数据源动态路由业务,帮助小伙伴们对动态代理加深一下印象。创建动态代理的类 OrderServiceDynamicProxy,代码如下:
public class OrderServiceDynamicProxy implements InvocationHandler {
private SimpleDateFormat yearFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy");
private Object target;
public Object getInstance(Object target){
this.target = target;
Class<?> clazz = target.getClass();
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(clazz.getClassLoader(),
clazz.getInterfaces(),this);
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)throws Throwable{
before(args[0]);
Object object = method.invoke(target,args);
after();
return object;
}
private void before(Object target){
try {
System.out.println("Proxy before method.");
Long time = (Long) target.getClass().
getMethod("getCreateTime").invoke(target);
Integer dbRouter = Integer.valueOf(yearFormat.format(new Date(time)));
System.out.println("静态代理类自动分配到【DB_" + dbRouter + "】数据源处理数据。");
DynamicDataSourceEntry.set(dbRouter);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void after(){
System.out.println("Proxy after method.");
}
}
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Order order = new Order();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Date date = sdf.parse("2018/02/01");
order.setCreateTime(date.getTime());
IOrderService orderService = (IOrderService)new OrderServiceDynamicProxy().getInstance(new OrderService());
orderService.createOrder(order);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
依然能够达到相同运行效果。但是,动态代理实现之后,我们不仅能实现 Order 的数据源动态路由,还可以实现其他任何类的数据源路由。当然,有比较重要的约定,必须要求实现 getCreateTime()方法,因为路由规则是根据时间来运算的。当然,我们可以通过接口规范来达到约束的目的,在此就不再举例。
高仿真 JDK Proxy 手写实现
不仅知其然,还得知其所以然。既然 JDK Proxy 功能如此强大,那么它是如何实现的呢?
我们现在来探究一下原理,并模仿 JDK Proxy 自己动手写一个属于自己的动态代理。
我们都知道 JDK Proxy 采用字节重组,重新生的对象来替代原始的对象以达到动态代理的目的。JDK Proxy 生成对象的步骤如下:
- 。
- 。
- 。
- 。
- 。
以上这个过程就叫字节码重组。JDK 中有一个规范,在 ClassPath 下只要是$开头的 class 文件一般都是自动生成的。那么我们有没有办法看到代替后的对象的真容呢?做一个这样测试,我们从内存中的对象字节码通过文件流输出到一个新的 class 文件,然后,利用反编译工具查看 class 的源代码。来看测试代码:
public class JDKProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Person obj = (Person)new JDKMeipo().getInstance(new Customer());
obj.findLove();
//通过反编译工具可以查看源代码
byte [] bytes = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass("$Proxy0",new Class[]{Person.class});
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E://$Proxy0.class");
os.write(bytes);
os.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行之后,我们能在 E://盘下找到一个 $Proxy0.class 文件。使用 Jad 反编译,得到 $Proxy0.jad 文件,打开可以看到如下内容:
// Decompiled by Jad v1.5.8g. Copyright 2001 Pavel Kouznetsov.
// Jad home page: http://www.kpdus.com/jad.html
// Decompiler options: packimports(3)
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements Person {
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler invocationhandler) {
super(invocationhandler);
}
public final boolean equals(Object obj) {
try{
return ((Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[] {
obj
})).booleanValue();
}
catch(Error _ex) { }
catch(Throwable throwable){
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final void findLove() {
try {
super.h.invoke(this, m3, null);
return;
}
catch(Error _ex) { }
catch(Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final String toString() {
try {
return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m2, null);
}
catch(Error _ex) { }
catch(Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final int hashCode() {
try {
return ((Integer)super.h.invoke(this, m0, null)).intValue();
}
catch(Error _ex) { }
catch(Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
private static Method m1;
private static Method m3;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m0;
static {
try {
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", new Class[] {
Class.forName("java.lang.Object")
});
m3 = Class.forName("com.gupaoedu.vip.pattern.proxy.Person").getMethod("findLove", new
Class[0]);
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString", new Class[0]);
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]);
}
catch(NoSuchMethodException nosuchmethodexception) {
throw new NoSuchMethodError(nosuchmethodexception.getMessage());
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException classnotfoundexception) {
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(classnotfoundexception.getMessage());
}
}
}
我们发现 $Proxy0 继承了 Proxy 类,同时还实现了我们的 Person 接口,而且重写了 findLove() 等方法。而且在静态块中用反射查找到了目标对象的所有方法,而且保存了所有方法的引用,在重写的方法用反射调用目标对象的方法。小伙伴们此时一定在好奇,这些代码是哪里来的呢?其实是 JDK 帮我们自动生成的。现在,我们不依赖 JDK 自己来动态生成源代码、动态完成编译,然后,替代目标对象并执行。
创建 GPInvocationHandler 接口:
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public interface GPInvocationHandler {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable;
}
创建 GPProxy 类:
/**
* 用来生成源代码的工具类
* Created by Tom.
*/
public class GPProxy {
public static final String ln = "\r\n";
public static Object newProxyInstance(GPClassLoader classLoader, Class<?> [] interfaces, GPInvocationHandler h){
try {
//1、动态生成源代码.java 文件
String src = generateSrc(interfaces);
// System.out.println(src);
//2、Java 文件输出磁盘
String filePath = GPProxy.class.getResource("").getPath();
// System.out.println(filePath);
File f = new File(filePath + "$Proxy0.java");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(f);
fw.write(src);
fw.flush();
fw.close();
//3、把生成的.java 文件编译成.class 文件
JavaCompiler compiler = ToolProvider.getSystemJavaCompiler();
StandardJavaFileManager manage =
compiler.getStandardFileManager(null,null,null);
Iterable iterable = manage.getJavaFileObjects(f);
JavaCompiler.CompilationTask task =
compiler.getTask(null,manage,null,null,null,iterable);
task.call();
manage.close();
//4、编译生成的.class 文件加载到 JVM 中来
Class proxyClass = classLoader.findClass("$Proxy0");
Constructor c = proxyClass.getConstructor(GPInvocationHandler.class);
f.delete();
//5、返回字节码重组以后的新的代理对象
return c.newInstance(h);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
private static String generateSrc(Class<?>[] interfaces){
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append("package com.gupaoedu.vip.pattern.proxy.dynamicproxy.gpproxy;" + ln);
sb.append("import com.gupaoedu.vip.pattern.proxy.Person;" + ln);
sb.append("import java.lang.reflect.*;" + ln);
sb.append("public class $Proxy0 implements " + interfaces[0].getName() + "{" + ln);
sb.append("GPInvocationHandler h;" + ln);
sb.append("public $Proxy0(GPInvocationHandler h) { " + ln);
sb.append("this.h = h;");
sb.append("}" + ln);
for (Method m : interfaces[0].getMethods()){
Class<?>[] params = m.getParameterTypes();
StringBuffer paramNames = new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer paramValues = new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer paramClasses = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
Class clazz = params[i];
String type = clazz.getName();
String paramName = toLowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
paramNames.append(type + " " + paramName);
paramValues.append(paramName);
paramClasses.append(clazz.getName() + ".class");
if(i > 0 && i < params.length-1){
paramNames.append(",");
paramClasses.append(",");
paramValues.append(",");
}
}
sb.append("public " + m.getReturnType().getName() + " " + m.getName() + "(" + paramNames.toString() + ") {" + ln);
sb.append("try{" + ln);
sb.append("Method m = " + interfaces[0].getName() + ".class.getMethod(\""
- m.getName() + "\",new Class[]{" + paramClasses.toString() + "});" + ln);
sb.append((hasReturnValue(m.getReturnType()) ? "return " : "") + getCaseCode("this.h.invoke(this,m,new Object[]{" + paramValues + "})",m.getReturnType()) + ";" + ln);
sb.append("}catch(Error _ex) { }");
sb.append("catch(Throwable e){" + ln);
sb.append("throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(e);" + ln);
sb.append("}");
sb.append(getReturnEmptyCode(m.getReturnType()));
sb.append("}");
}
sb.append("}" + ln);
return sb.toString();
}
private static Map<Class,Class> mappings = new HashMap<Class, Class>();
static {
mappings.put(int.class,Integer.class);
}
private static String getReturnEmptyCode(Class<?> returnClass){
if(mappings.containsKey(returnClass)){
return "return 0;";
}else if(returnClass == void.class){
return "";
}else {
return "return null;";
}
}
private static String getCaseCode(String code,Class<?> returnClass){
if(mappings.containsKey(returnClass)){
return "((" + mappings.get(returnClass).getName() + ")" + code + ")." +
returnClass.getSimpleName() + "Value()";
}
return code;
}
private static boolean hasReturnValue(Class<?> clazz){
return clazz != void.class;
}
private static String toLowerFirstCase(String src){
char [] chars = src.toCharArray();
chars[0] += 32;
return String.valueOf(chars);
}
}
创建 GPClassLoader 类:
public class GPClassLoader extends ClassLoader{
private File classPathFile;
public GPClassLoader(){
String classPath = GPClassLoader.class.getResource("").getPath();
this.classPathFile = new File(classPath);
}
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
String className = GPClassLoader.class.getPackage().getName() + "." + name;
if(classPathFile != null){
File classFile = new File(classPathFile,name.replaceAll("\\.","/") + ".class");
if(classFile.exists()){
FileInputStream in = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream out = null;
try{
in = new FileInputStream(classFile);
out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte [] buff = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = in.read(buff)) != -1){
out.write(buff,0,len);
}
return defineClass(className,out.toByteArray(),0,out.size());
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != in){
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(out != null){
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
创建 GPMeipo 类:
public class GPMeipo implements GPInvocationHandler {
//被代理的对象,把引用给保存下来
private Object target;
public Object getInstance(Object target) throws Exception{
this.target = target;
Class<?> clazz = target.getClass();
return GPProxy.newProxyInstance(new GPClassLoader(),
clazz.getInterfaces(),this);
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)throws Throwable{
before();
method.invoke(this.target,args);
after();
return null;
}
private void before(){
System.out.println("我是媒婆:我要给你找对象,现在已经拿到你的需求");
System.out.println("开始物色");
}
private void after(){
System.out.println("如果合适的话,就准备办事");
}
}
客户端测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Person obj = (Person)new GPMeipo().getInstance(new Customer());
System.out.println(obj.getClass());
obj.findLove();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
到此,手写 JDK 动态代理就完成了。小伙伴们,是不是又多了一个面试用的杀手锏呢?
CGLIB 动态代理
CGLib 调用 及原理分析
简单看一下 CGLib 代理的使用,还是以媒婆为例,创建 CglibMeipo 类:
public class CglibMeipo implements MethodInterceptor{
public Object getInstance(Class<?> clazz) throws Exception{
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
//要把哪个设置为即将生成的新类父类
enhancer.setSuperclass(clazz);
enhancer.setCallback(this);
return enhancer.create();
}
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
//业务的增强
before();
Object obj = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o,objects);
after();
return obj;
}
private void before(){
System.out.println("我是媒婆:我要给你找对象,现在已经拿到你的需求");
System.out.println("开始物色");
}
private void after(){
System.out.println("如果合适的话,就准备办事");
}
}
创建单身客户 Customer 类:
public class Customer {
public void findLove(){
System.out.println("肤白貌美大象腿");
}
}
有个小细节,CGLib 代理的目标对象不需要实现任何接口,它是通过动态继承目标对象实现的动态代理。来看测试代码:
public class CglibTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Customer obj = (Customer)new CglibMeipo().getInstance(Customer.class);
obj.findLove();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
CGLib 的实现原理又是怎样的呢?我们可以在测试代码中加上一句代码,将 CGLib 代理后的 class 写入到磁盘,然后,我们再反编译一探究竟,代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//利用 cglib 的代理类可以将内存中的 class 文件写入本地磁盘
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY,
"E://cglib_proxy_class/");
Customer obj = (Customer)new CglibMeipo().getInstance(Customer.class);
obj.findLove();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
重新执行代码,我们会发现在 E://cglib_proxy_class 目录下多了三个 class 文件,如图:
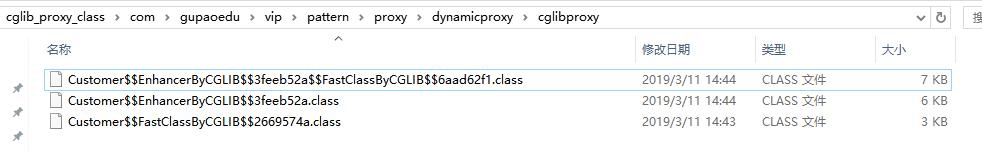
通过调试跟踪,我们发现 Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a.class 就是 CGLib 生成的代理类,继承了 Customer 类。反编译后代码是这样的:
// Decompiled by Jad v1.5.8g. Copyright 2001 Pavel Kouznetsov.
// Jad home page: http://www.kpdus.com/jad.html
// Decompiler options: packimports(3)
// Source File Name: <generated>
// ...
// Customer
public class Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a extends Customer implements Factory{
static void CGLIB$STATICHOOK1(){
Method amethod[];
Method amethod1[];
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS = new ThreadLocal();
CGLIB$emptyArgs = new Object[0];
Class class1 = Class.forName("com.gupaoedu.vip.pattern.proxy.dynamicproxy.cglibproxy.Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a");
Class class2;
amethod = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[] {
"findLove", "()V"
}, (class2 = Class.forName("com.gupaoedu.vip.pattern.proxy.dynamicproxy.cglibproxy.Customer")).getDeclaredMethods());
Method[] _tmp = amethod;
CGLIB$findLove$0$Method = amethod[0];
CGLIB$findLove$0$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "()V", "findLove", "CGLIB$findLove$0");
amethod1 = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[] {"finalize", "()V", "equals", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;",
"hashCode", "()I", "clone", "()Ljava/lang/Object;"}, (class2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object")).getDeclaredMethods());
Method[] _tmp1 = amethod1;
CGLIB$finalize$1$Method = amethod1[0];
CGLIB$finalize$1$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "()V", "finalize", "CGLIB$finalize$1");
CGLIB$equals$2$Method = amethod1[1];
CGLIB$equals$2$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z","equals", "CGLIB$equals$2");
CGLIB$toString$3$Method = amethod1[2];
CGLIB$toString$3$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "()Ljava/lang/String;", "toString", "CGLIB$toString$3");
CGLIB$hashCode$4$Method = amethod1[3];
CGLIB$hashCode$4$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "()I", "hashCode", "CGLIB$hashCode$4");
CGLIB$clone$5$Method = amethod1[4];
CGLIB$clone$5$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(class2, class1, "()Ljava/lang/Object;", "clone", "CGLIB$clone$5");
}
final void CGLIB$findLove$0(){
super.findLove();
}
public final void findLove(){
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if(CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 != null) goto _L2; else goto _L1
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
_L2:
JVM INSTR dup ;
JVM INSTR ifnull 37;
goto _L3 _L4
_L3:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_21;
_L4:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_37;
this;
CGLIB$findLove$0$Method;
CGLIB$emptyArgs;
CGLIB$findLove$0$Proxy;
intercept();
return;
super.findLove();
return;
}
final void CGLIB$finalize$1()throws Throwable{
super.finalize();
}
protected final void finalize()throws Throwable{
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if(CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 != null) goto _L2; else goto _L1
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
_L2:
JVM INSTR dup ;
JVM INSTR ifnull 37;
goto _L3 _L4
_L3:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_21;
_L4:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_37;
this;
CGLIB$finalize$1$Method;
CGLIB$emptyArgs;
CGLIB$finalize$1$Proxy;
intercept();
return;
super.finalize();
return;
}
final boolean CGLIB$equals$2(Object obj){
return super.equals(obj);
}
public final boolean equals(Object obj) {
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if(CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 != null) goto _L2; else goto _L1
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
_L2:
JVM INSTR dup ;
JVM INSTR ifnull 57;
goto _L3 _L4
_L3:
this;
CGLIB$equals$2$Method;
new Object[] {
obj
};
CGLIB$equals$2$Proxy;
intercept();
JVM INSTR dup ;
JVM INSTR ifnonnull 50;
goto _L5 _L6
_L5:
JVM INSTR pop ;
false;
goto _L7
_L6:
(Boolean);
booleanValue();
_L7:
return;
_L4:
return super.equals(obj);
}
final String CGLIB$toString$3(){
return super.toString();
}
public final String toString(){
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if(CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 != null) goto _L2; else goto _L1
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
_L2:
JVM INSTR dup ;
JVM INSTR ifnull 40;
goto _L3 _L4
_L3:
this;
CGLIB$toString$3$Method;
CGLIB$emptyArgs;
CGLIB$toString$3$Proxy;
intercept();
(String);
return;
_L4:
return super.toString();
}
final int CGLIB$hashCode$4(){
return super.hashCode();
}
public final int hashCode(){
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if(CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 != null) goto _L2; else goto _L1
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
_L2:
JVM INSTR dup ;
JVM INSTR ifnull 52;
goto _L3 _L4
_L3:
this;
CGLIB$hashCode$4$Method;
CGLIB$emptyArgs;
CGLIB$hashCode$4$Proxy;
intercept();
JVM INSTR dup ;
JVM INSTR ifnonnull 45;
goto _L5 _L6
_L5:
JVM INSTR pop ;
0;
goto _L7
_L6:
(Number);
intValue();
_L7:
return;
_L4:
return super.hashCode();
}
final Object CGLIB$clone$5() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
protected final Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if(CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 != null) goto _L2; else goto _L1
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
_L2:
JVM INSTR dup ;
JVM INSTR ifnull 37;
goto _L3 _L4
_L3:
this;
CGLIB$clone$5$Method;
CGLIB$emptyArgs;
CGLIB$clone$5$Proxy;
intercept();
return;
_L4:
return super.clone();
}
public static MethodProxy CGLIB$findMethodProxy(Signature signature) {
String s = signature.toString();
s;
s.hashCode();
JVM INSTR lookupswitch 6: default 140
// -1574182249: 68
// -508378822: 80
// 1192015562: 92
// 1826985398: 104
// 1913648695: 116
// 1984935277: 128;
goto _L1 _L2 _L3 _L4 _L5 _L6 _L7
_L2:
"finalize()V";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 141;
goto _L8 _L9
_L9:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_141;
_L8:
return CGLIB$finalize$1$Proxy;
_L3:
"clone()Ljava/lang/Object;";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 141;
goto _L10 _L11
_L11:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_141;
_L10:
return CGLIB$clone$5$Proxy;
_L4:
"findLove()V";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 141;
goto _L12 _L13
_L13:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_141;
_L12:
return CGLIB$findLove$0$Proxy;
_L5:
"equals(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 141;
goto _L14 _L15
_L15:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_141;
_L14:
return CGLIB$equals$2$Proxy;
_L6:
"toString()Ljava/lang/String;";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 141;
goto _L16 _L17
_L17:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_141;
_L16:
return CGLIB$toString$3$Proxy;
_L7:
"hashCode()I";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 141;
goto _L18 _L19
_L19:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_141;
_L18:
return CGLIB$hashCode$4$Proxy;
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
return null;
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(Callback acallback[]){
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.set(acallback);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_STATIC_CALLBACKS(Callback acallback[]){
CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS = acallback;
}
private static final void CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(Object obj){
Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a customer$$enhancerbycglib$$3feeb52a =
(Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a)obj;
if(customer$$enhancerbycglib$$3feeb52a.CGLIB$BOUND) goto _L2; else goto _L1
_L1:
Object obj1;
customer$$enhancerbycglib$$3feeb52a.CGLIB$BOUND = true;
obj1 = CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.get();
obj1;
if(obj1 != null) goto _L4; else goto _L3
_L3:
JVM INSTR pop ;
CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
if(CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS != null) goto _L4; else goto _L5
_L5:
JVM INSTR pop ;
goto _L2
_L4:
(Callback[]);
customer$$enhancerbycglib$$3feeb52a;
JVM INSTR swap ;
0;
JVM INSTR aaload ;
(MethodInterceptor);
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
_L2:
}
public Object newInstance(Callback acallback[]){
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(acallback);
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return new Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a();
}
public Object newInstance(Callback callback){
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(new Callback[] {
callback
});
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return new Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a();
}
public Object newInstance(Class aclass[], Object aobj[], Callback acallback[]){
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(acallback);
JVM INSTR new #2 <Class Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a>;
JVM INSTR dup ;
aclass;
aclass.length;
JVM INSTR tableswitch 0 0: default 35
// 0 28;
goto _L1 _L2
_L2:
JVM INSTR pop ;
Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a();
goto _L3
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Constructor not found");
_L3:
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return;
}
public Callback getCallback(int i){
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
this;
i;
JVM INSTR tableswitch 0 0: default 30
// 0 24;
goto _L1 _L2
_L2:
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
goto _L3
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
null;
_L3:
return;
}
public void setCallback(int i, Callback callback){
switch(i){
case 0: // '\0'
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)callback;
break;
}
}
public Callback[] getCallbacks(){
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
this;
return (new Callback[] {
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0
});
}
public void setCallbacks(Callback acallback[]){
this;
acallback;
JVM INSTR dup2 ;
0;
JVM INSTR aaload ;
(MethodInterceptor);
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
private boolean CGLIB$BOUND;
private static final ThreadLocal CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS;
private static final Callback CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS[];
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
private static final Method CGLIB$findLove$0$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$findLove$0$Proxy;
private static final Object CGLIB$emptyArgs[];
private static final Method CGLIB$finalize$1$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$finalize$1$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$equals$2$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$equals$2$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$toString$3$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$toString$3$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$hashCode$4$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$hashCode$4$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$clone$5$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$clone$5$Proxy;
static{
CGLIB$STATICHOOK1();
}
public Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a(){
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
}
重写了 Customer 类的所有方法。我们通过代理类的源码可以看到,代理类会获得所有在 父 类 继 承 来 的 方 法 , 并 且 会 有 MethodProxy 与 之 对 应 , 比 如 Method CGLIB$findLove$0$Method、MethodProxy CGLIB$findLove$0$Proxy;这些方法在代理类的 findLove() 中都有调用。
//代理方法(methodProxy.invokeSuper 会调用)
final void CGLIB$findLove$0(){
super.findLove();
}
//被代理方法(methodProxy.invoke 会调用,这就是为什么在拦截器中调用 methodProxy.invoke 会死循环,一直在调用拦截器)
public final void findLove(){
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if(CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 != null) goto _L2; else goto _L1
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
_L2:
JVM INSTR dup ;
JVM INSTR ifnull 37;
goto _L3 _L4
_L3:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_21;
_L4:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_37;
this;
CGLIB$findLove$0$Method;
CGLIB$emptyArgs;
CGLIB$findLove$0$Proxy;
//调用拦截器
intercept();
return;
super.findLove();
return;
}
调 用 过 程 : 代 理 对 象 调 用 this.findLove() 方 法 -> 调 用 拦 截 器 -> methodProxy.invokeSuper->CGLIB$findLove$0->被代理对象 findLove()方法。
此时,我们发现拦截器 MethodInterceptor 中就是由 MethodProxy 的 invokeSuper 方法调用代理方法的,MethodProxy 非常关键,我们分析一下它具体做了什么。
public class MethodProxy {
private Signature sig1;
private Signature sig2;
private MethodProxy.CreateInfo createInfo;
private final Object initLock = new Object();
private volatile MethodProxy.FastClassInfo fastClassInfo;
public static MethodProxy create(Class c1, Class c2, String desc, String name1, String name2) {
MethodProxy proxy = new MethodProxy();
proxy.sig1 = new Signature(name1, desc);
proxy.sig2 = new Signature(name2, desc);
proxy.createInfo = new MethodProxy.CreateInfo(c1, c2);
return proxy;
}
...
private static class CreateInfo {
Class c1;
Class c2;
NamingPolicy namingPolicy;
GeneratorStrategy strategy;
boolean attemptLoad;
public CreateInfo(Class c1, Class c2) {
this.c1 = c1;
this.c2 = c2;
AbstractClassGenerator fromEnhancer = AbstractClassGenerator.getCurrent();
if(fromEnhancer != null) {
this.namingPolicy = fromEnhancer.getNamingPolicy();
this.strategy = fromEnhancer.getStrategy();
this.attemptLoad = fromEnhancer.getAttemptLoad();
}
}
}
...
}
继续看 invokeSuper()方法:
public Object invokeSuper(Object obj, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
this.init();
MethodProxy.FastClassInfo fci = this.fastClassInfo;
return fci.f2.invoke(fci.i2, obj, args);
} catch (InvocationTargetException var4) {
throw var4.getTargetException();
}
}
...
private static class FastClassInfo {
FastClass f1;
FastClass f2;
int i1;
int i2;
private FastClassInfo() {
}
}
上面代码调用过程就是获取到代理类对应的 FastClass,并执行了代理方法。还记得之前生成三个 class 文件吗?
Customer$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$3feeb52a$$FastClassByCGLIB$$6aad62f1.class就 是代理类的 FastClass,Customer$$FastClassByCGLIB$$2669574a.class 就是被代理类的 FastClass。
CGLib 动态代理执行代理方法效率之所以比 JDK 的高是因为 Cglib 采用了 FastClass 机制,它的原理简单来说就是:为代理类和被代理类各生成一个 Class,这个 Class 会为代理类或被代理类的方法分配一个 index(int 类型)。这个 index 当做一个入参,FastClass 就可以直接定位要调用的方法直接进行调用,这样省去了反射调用,所以调用效率比 JDK 动态代理通过反射调用高。下面我们反编译一个 FastClass 看看:
public int getIndex(Signature signature){
String s = signature.toString();
s;
s.hashCode();
JVM INSTR lookupswitch 11: default 223
// -1725733088: 108
// -1310345955: 119
// -1026001249: 129
// 243996900: 139
// 946854621: 149
// 1116248544: 160
// 1192015562: 170
// 1826985398: 180
// 1902039948: 190
// 1913648695: 201
// 1984935277: 212;
goto _L1 _L2 _L3 _L4 _L5 _L6 _L7 _L8 _L9 _L10 _L11 _L12
_L2:
"getClass()Ljava/lang/Class;";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L13 _L14
_L14:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L13:
return 8;
_L3:
"eat()V";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L15 _L16
_L16:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L15:
return 0;
_L4:
"wait(JI)V";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L17 _L18
_L18:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L17:
return 3;
_L5:
"wait(J)V";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L19 _L20
_L20:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L19:
return 4;
_L6:
"notifyAll()V";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L21 _L22
_L22:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L21:
return 10;
_L7:
"wait()V";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L23 _L24
_L24:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L23:
return 2;
_L8:
"findLove()V";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L25 _L26
_L26:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L25:
return 1;
_L9:
"equals(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L27 _L28
_L28:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L27:
return 5;
_L10:
"notify()V";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L29 _L30
_L30:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L29:
return 9;
_L11:
"toString()Ljava/lang/String;";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L31 _L32
_L32:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L31:
return 6;
_L12:
"hashCode()I";
equals();
JVM INSTR ifeq 224;
goto _L33 _L34
_L34:
break MISSING_BLOCK_LABEL_224;
_L33:
return 7;
_L1:
JVM INSTR pop ;
return -1;
}
//部分代码省略...
//根据 index 直接定位执行方法
public Object invoke(int i, Object obj, Object aobj[])throws InvocationTargetException{
(Customer)obj;
i;
JVM INSTR tableswitch 0 10: default 161
// 0 64
// 1 69
// 2 74
// 3 79
// 4 102
// 5 116
// 6 131
// 7 135
// 8 147
// 9 151
// 10 156;
goto _L1 _L2 _L3 _L4 _L5 _L6 _L7 _L8 _L9 _L10 _L11 _L12
_L2:
eat();
return null;
_L3:
findLove();
return null;
_L4:
wait();
return null;
_L5:
((Number)aobj[0]).longValue();
((Number)aobj[1]).intValue();
wait();
return null;
_L6:
((Number)aobj[0]).longValue();
wait();
return null;
_L7:
aobj[0];
equals();
JVM INSTR new #106 <Class Boolean>;
JVM INSTR dup_x1 ;
JVM INSTR swap ;
Boolean();
return;
_L8:
toString();
return;
_L9:
hashCode();
JVM INSTR new #113 <Class Integer>;
JVM INSTR dup_x1 ;
JVM INSTR swap ;
Integer();
return;
_L10:
getClass();
return;
_L11:
notify();
return null;
_L12:
notifyAll();
return null;
JVM INSTR new #79 <Class InvocationTargetException>;
JVM INSTR dup_x1 ;
JVM INSTR swap ;
InvocationTargetException();
throw ;
_L1:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot find matching method/constructor");
}
FastClass 并不是跟代理类一块生成的,而是在第一次执行 MethodProxy invoke/invokeSuper 时生成的并放在了缓存中。
//MethodProxy invoke/invokeSuper 都调用了 init()
private void init() {
if(this.fastClassInfo == null) {
Object var1 = this.initLock;
synchronized(this.initLock) {
if(this.fastClassInfo == null) {
MethodProxy.CreateInfo ci = this.createInfo;
MethodProxy.FastClassInfo fci = new MethodProxy.FastClassInfo();
fci.f1 = helper(ci, ci.c1);//如果缓存中就取出,没有就生成新的 FastClass
fci.f2 = helper(ci, ci.c2);
fci.i1 = fci.f1.getIndex(this.sig1);//获取方法的 index
fci.i2 = fci.f2.getIndex(this.sig2);
this.fastClassInfo = fci;
}
}
}
}
至此,Cglib 动态代理的原理我们就基本搞清楚了,如果对代码细节有兴趣的小伙伴可以再自行深入研究。
CGLib 和 JDK 动态代理对比
- JDK 动态代理是实现了被代理对象的接口,CGLib 是继承了被代理对象。
- JDK 和 CGLib 都是在运行期生成字节码,JDK 是直接写 Class 字节码,CGLib 使用 ASM 框架写 Class 字节码,Cglib 代理实现更复杂,生成代理类比 JDK 效率低。
- JDK 调用代理方法,是通过反射机制调用,CGLib 是通过 FastClass 机制直接调用方法,CGLib 执行效率更高。
代理模式与 Spring
代理模式在 Spring 中的应用
先看 ProxyFactoryBean 核心的方法就是 getObject()方法,我们来看一下源码:
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
initializeAdvisorChain();
if (isSingleton()) {
return getSingletonInstance();
}
else {
if (this.targetName == null) {
logger.warn("Using non-singleton proxies with singleton targets is often undesirable. " + "Enable prototype proxies by setting the 'targetName' property.");
}
return newPrototypeInstance();
}
}
在 getObject()方法中,主要调用 getSingletonInstance()和 newPrototypeInstance();
在 Spring 的配置中,如果不做任何设置,那么 Spring 代理生成的 Bean 都是单例对象。如果修改 scope 则每次创建一个新的原型对象。newPrototypeInstance() 里面的逻辑比较复杂,我们后面的课程再做深入研究,这里我们先做简单的了解。
Spring 利用动态代理实现 AOP 有两个非常重要的类,一个是 JdkDynamicAopProxy 类 和 CglibAopProxy 类,来看一下类图:
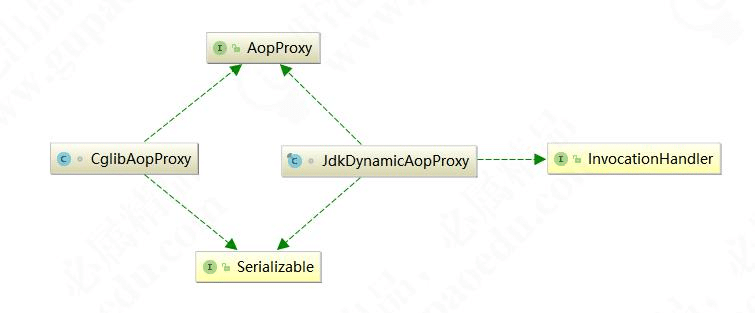
Spring 中的代理选择原则
- 当 Bean 有实现接口时,Spring 就会用 JDK 的动态代理
- 当 Bean 没有实现接口时,Spring 选择 CGLib。
- Spring 可以通过配置强制使用 CGLib,只需在 Spring 的配置文件中加入如下代码:
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>
参考资料
静态代理和动态的本质区别
- 静态代理只能通过手动完成代理操作,如果被代理类增加新的方法,代理类需要同步新增,违背开闭原则。
- 动态代理采用在运行时动态生成代码的方式,取消了对被代理类的扩展限制,遵循开闭原则。
- 若动态代理要对目标类的增强逻辑扩展,结合策略模式,只需要新增策略类便可完成,无需修改代理类的代码。
代理模式的优缺点
使用代理模式具有以下几个优点:
- 代理模式能将代理对象与真实被调用的目标对象分离。
- 一定程度上降低了系统的耦合度,扩展性好。
- 可以起到保护目标对象的
- 对目标对象的功能增强。
当然,代理模式也是有缺点的:
- 代理模式会造成系统设计中类的数量增加。
- 在客户端和目标对象增加一个代理对象,会造成请求处理速度变慢。
- 增加了系统的复杂度。